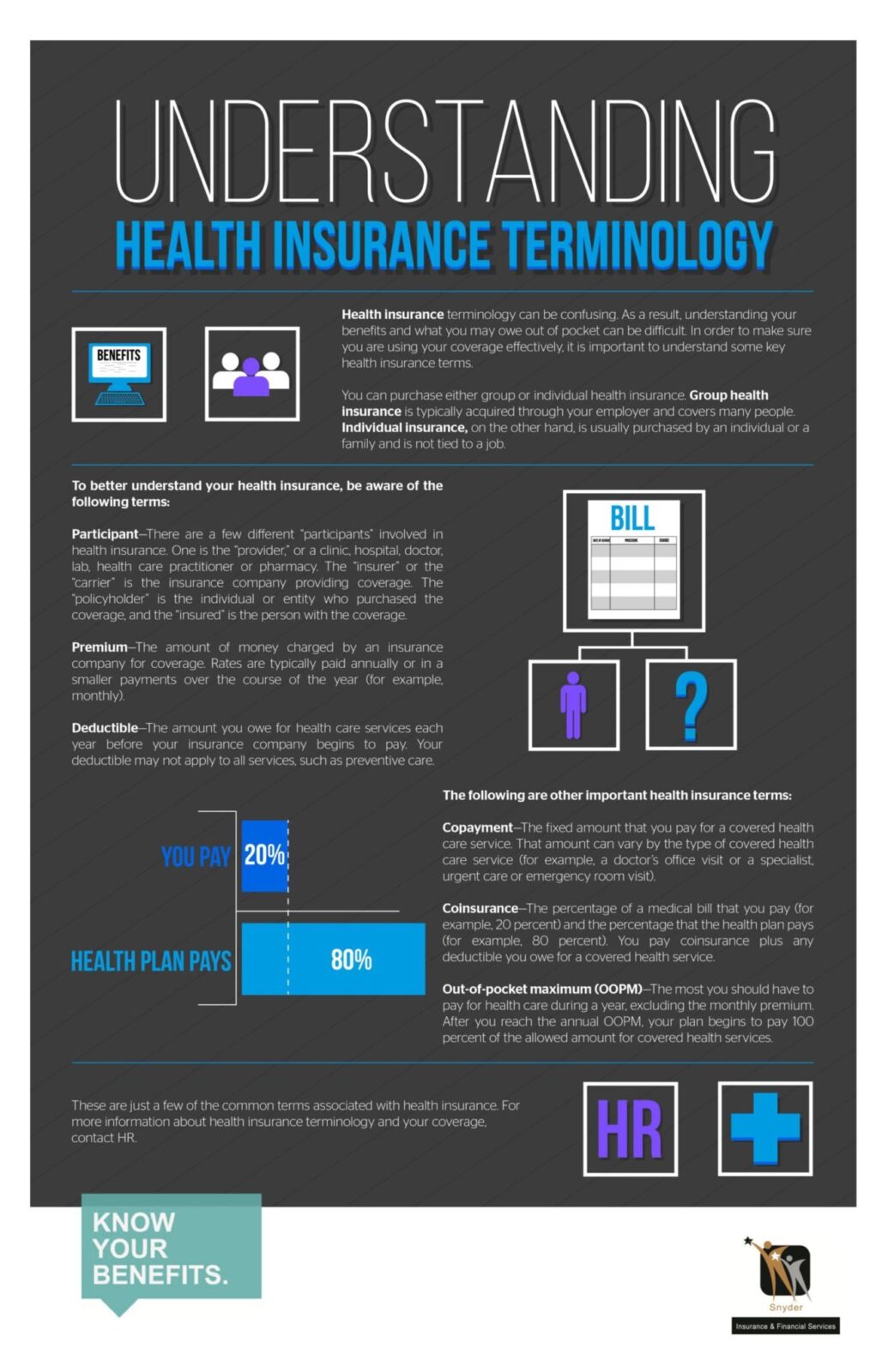
Health Insurance Terminology
Health insurance benefits can be confusing. Where do I go for urgent care? What is the difference between long-term care and custodial care?
In order to get the most out of your employer-sponsored health insurance benefits, and to be sure that you are getting the most cost-effective care, it is important to understand the terms you will find in your plan booklet.
Health Care Facilities Defined
Ambulatory setting – institutions such as surgery centers, clinics or other outpatient facilities that provide outpatient health care services.
Approved health care facility or program – a facility or program that is licensed, certified or otherwise authorized according to the laws of the state to provide health care, and which has been approved by a health plan as described in the contract.
Extended care facility – a nursing home or nursing center that is licensed to operate in accordance with all applicable state and local laws and that provides 24-hour nursing care. These facilities offer skilled intermediate or custodial care, or any combination of these types of care.
Facility – a physical location where health care services are provided, such as a hospital, clinic, emergency room or ambulatory care center.
Home health agency (HHA) – a state and federally certified facility that is approved to provide health care services in the home.
Hospice – a facility or program that is primarily designed to provide pain relief, symptom management and supportive services for the terminally ill and their families.
Intermediate care facility – a facility that is licensed by the state and provides nursing care to patients who require a degree of care that is less than would be received in a hospital or skilled nursing facility, but more than room and board.
Long-term care facility – usually a state licensed facility that provides skilled nursing services, intermediate care and custodial care.
Nursing home – a licensed facility that provides general nursing care to chronically ill patients who are unable to care for themselves and their daily living needs. Also referred to as a long-term care facility.
Outpatient surgical center – a health care facility, separate from a hospital, that provides pre-scheduled outpatient surgical services. Also called a freestanding outpatient surgical center or day-surgery center.
Skilled nursing facility – a facility either freestanding or part of a hospital, which provides rehabilitation and medical care that is less intense than would be provided in a hospital.
Sub-acute care facility – an intermediate care facility which provides care for patients too ill to be released to long-term care or their homes, but not so ill that they require ongoing hospitalization.
Treatment facility – any residential or non-residential facility that is authorized to provide treatment for mental health conditions or substance abuse.
Urgent care center – a health care facility whose primary purpose is the provision of immediate, short-term medical care for minor but urgent medical conditions. Serves as an alternative to the hospital emergency room.
Types of Care Defined
Activities of daily living (ADL) – everyday living functions and activities performed by individuals without assistance, including walking, dressing, personal hygiene and eating.
Acute care – skilled medical care provided by medical and nursing personnel in order to restore a person to good health.
Adult day care – a type of care (usually custodial) for individuals who require assistance with various activities of daily living while their primary caregivers are absent.
Aftercare – patient services required after hospitalization or rehabilitation.
Ambulatory care – care given on an outpatient basis.
Ancillary care – additional services (other than room and board) performed relating to a specific incident of care. Includes services such as x-rays, lab work, radiology, and anesthesia.
Behavioral health care – assessment and treatment of mental illness or substance abuse disorders.
Custodial care – care primarily to meet a patient’s personal needs, such as bathing, dressing, eating, or taking medicine. Can be provided by medical or non-medical personnel, but must be administered according to a doctor’s order.
Emergency services – services provided for an unforeseen acute illness or injury that requires immediate medical attention.
Home health care – skilled or unskilled care provided in an individual’s home, usually on a part-time basis. Examples include part-time skilled nursing care, speech therapy, physical or occupational therapy, part-time services from home health aides or assistance with household chores.
Hospice services – services provided to the terminally ill and their families.
Intermediate nursing care – health or medical care that is occasional or rehabilitative, ordered by a physician and performed by skilled medical personnel.
Long-term care – care provided to people with chronic diseases or disabilities who need assistance with daily activities for an extended period. Includes a wide range of health and social services provided under the supervision of medical professionals.
Office visit – services provided in a physician’s office.
Outpatient services – care received in a hospital or ambulatory care center that does not require an overnight stay.
Preventive care – proactive, comprehensive care emphasizing prevention, early detection, and early treatment of conditions. Generally includes routine physical exams, immunizations and well-person care.
Primary care – basic or general health care, traditionally provided by family practice physicians, pediatricians or internal medicine practitioners.
Respite care – temporary health or medical care designed to provide a short rest period for a caregiver of a chronically or terminally ill person.
Secondary care – medical services provided by doctors who do not have first contact with patients, such as urologists, cardiologists and so on.
Specialty care – services delivered by a health care provider who has received advanced training in a specific field of medicine. Specialty care also includes care provided in specialty facilities and emergency care.
Tertiary care – health care services provided by highly specialized providers, such as neurosurgeons, thoracic surgeons and intensive care units. These services often require highly sophisticated technologies and facilities.